守護(hù)進(jìn)程是什么?linux創(chuàng)建守護(hù)進(jìn)程的步驟詳解
守護(hù)進(jìn)程是什么?可能很多伙伴對(duì)于守護(hù)進(jìn)程都不怎么了解吧?守護(hù)進(jìn)程是操作系統(tǒng)后臺(tái)的一種特殊進(jìn)程,像Linux系統(tǒng)的大多數(shù)服務(wù)器都是通過守護(hù)進(jìn)程實(shí)現(xiàn)的。今天小編就來給大家科普一下什么是守護(hù)進(jìn)程以及l(fā)inux系統(tǒng)如何創(chuàng)建守護(hù)進(jìn)程。
一、守護(hù)進(jìn)程是什么?
Linux Daemon(守護(hù)進(jìn)程)是運(yùn)行在后臺(tái)的一種特殊進(jìn)程。它獨(dú)立于控制終端并且周期性地執(zhí)行某種任務(wù)或等待處理某些發(fā)生的事件。它不需要用戶輸入就能運(yùn)行而且提供某種服務(wù),不是對(duì)整個(gè)系統(tǒng)就是對(duì)某個(gè)用戶程序提供服務(wù)。Linux系統(tǒng)的大多數(shù)服務(wù)器就是通過守護(hù)進(jìn)程實(shí)現(xiàn)的。常見的守護(hù)進(jìn)程包括系統(tǒng)日志進(jìn)程syslogd、 web服務(wù)器httpd、郵件服務(wù)器sendmail和數(shù)據(jù)庫服務(wù)器mysqld等。
守護(hù)進(jìn)程一般在系統(tǒng)啟動(dòng)時(shí)開始運(yùn)行,除非強(qiáng)行終止,否則直到系統(tǒng)關(guān)機(jī)都保持運(yùn)行。守護(hù)進(jìn)程經(jīng)常以超級(jí)用戶(root)權(quán)限運(yùn)行,因?yàn)樗鼈円褂锰厥獾亩丝冢?-1024)或訪問某些特殊的資源。
一個(gè)守護(hù)進(jìn)程的父進(jìn)程是init進(jìn)程,因?yàn)樗嬲母高M(jìn)程在fork出子進(jìn)程后就先于子進(jìn)程exit退出了,所以它是一個(gè)由init繼承的孤兒進(jìn)程。守護(hù)進(jìn)程是非交互式程序,沒有控制終端,所以任何輸出,無論是向標(biāo)準(zhǔn)輸出設(shè)備stdout還是標(biāo)準(zhǔn)出錯(cuò)設(shè)備stderr的輸出都需要特殊處理。
守護(hù)進(jìn)程的名稱通常以d結(jié)尾,比如sshd、xinetd、crond等
二、創(chuàng)建守護(hù)進(jìn)程的步驟
首先我們要了解一些基本概念:
1、進(jìn)程組 :
每個(gè)進(jìn)程也屬于一個(gè)進(jìn)程組
每個(gè)進(jìn)程主都有一個(gè)進(jìn)程組號(hào),該號(hào)等于該進(jìn)程組組長的PID號(hào) 。
一個(gè)進(jìn)程只能為它自己或子進(jìn)程設(shè)置進(jìn)程組ID號(hào)
2、會(huì)話期:
會(huì)話期(session)是一個(gè)或多個(gè)進(jìn)程組的集合。
setsid()函數(shù)可以建立一個(gè)對(duì)話期:
如果,調(diào)用setsid的進(jìn)程不是一個(gè)進(jìn)程組的組長,此函數(shù)創(chuàng)建一個(gè)新的會(huì)話期。
(1)此進(jìn)程變成該對(duì)話期的首進(jìn)程
(2)此進(jìn)程變成一個(gè)新進(jìn)程組的組長進(jìn)程。
(3)此進(jìn)程沒有控制終端,如果在調(diào)用setsid前,該進(jìn)程有控制終端,那么與該終端的聯(lián)系被解除。 如果該進(jìn)程是一個(gè)進(jìn)程組的組長,此函數(shù)返回錯(cuò)誤。
(4)為了保證這一點(diǎn),我們先調(diào)用fork()然后exit(),此時(shí)只有子進(jìn)程在運(yùn)行
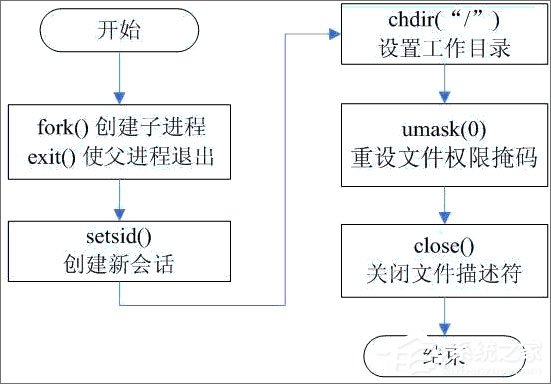
現(xiàn)在我們來給出創(chuàng)建守護(hù)進(jìn)程的所需步驟:
編寫守護(hù)進(jìn)程的一般步驟:
(1)在父進(jìn)程中執(zhí)行fork并exit推出;
(2)在子進(jìn)程中調(diào)用setsid函數(shù)創(chuàng)建新的會(huì)話;
(3)在子進(jìn)程中調(diào)用chdir函數(shù),讓根目錄 ”/” 成為子進(jìn)程的工作目錄;
(4)在子進(jìn)程中調(diào)用umask函數(shù),設(shè)置進(jìn)程的umask為0;
(5)在子進(jìn)程中關(guān)閉任何不需要的文件描述符
說明:
(1)在后臺(tái)運(yùn)行。
為避免掛起控制終端將Daemon放入后臺(tái)執(zhí)行。方法是在進(jìn)程中調(diào)用fork使父進(jìn)程終止,讓Daemon在子進(jìn)程中后臺(tái)執(zhí)行。
if(pid=fork())
exit(0);//是父進(jìn)程,結(jié)束父進(jìn)程,子進(jìn)程繼續(xù)
(2)脫離控制終端,登錄會(huì)話和進(jìn)程組
有必要先介紹一下Linux中的進(jìn)程與控制終端,登錄會(huì)話和進(jìn)程組之間的關(guān)系:進(jìn)程屬于一個(gè)進(jìn)程組,進(jìn)程組號(hào)(GID)就是進(jìn)程組長的進(jìn)程號(hào)(PID)。登錄會(huì)話可以包含多個(gè)進(jìn)程組。這些進(jìn)程組共享一個(gè)控制終端。這個(gè)控制終端通常是創(chuàng)建進(jìn)程的登錄終端。
控制終端,登錄會(huì)話和進(jìn)程組通常是從父進(jìn)程繼承下來的。我們的目的就是要擺脫它們,使之不受它們的影響。方法是在第1點(diǎn)的基礎(chǔ)上,調(diào)用setsid()使進(jìn)程成為會(huì)話組長:
setsid();
說明:當(dāng)進(jìn)程是會(huì)話組長時(shí)setsid()調(diào)用失敗。但第一點(diǎn)已經(jīng)保證進(jìn)程不是會(huì)話組長。setsid()調(diào)用成功后,進(jìn)程成為新的會(huì)話組長和新的進(jìn)程組長,并與原來的登錄會(huì)話和進(jìn)程組脫離。由于會(huì)話過程對(duì)控制終端的獨(dú)占性,進(jìn)程同時(shí)與控制終端脫離。
(3) 禁止進(jìn)程重新打開控制終端
現(xiàn)在,進(jìn)程已經(jīng)成為無終端的會(huì)話組長。但它可以重新申請(qǐng)打開一個(gè)控制終端。可以通過使進(jìn)程不再成為會(huì)話組長來禁止進(jìn)程重新打開控制終端:
if(pid=fork())
exit(0);//結(jié)束第一子進(jìn)程,第二子進(jìn)程繼續(xù)(第二子進(jìn)程不再是會(huì)話組長)
(4)關(guān)閉打開的文件描述符
進(jìn)程從創(chuàng)建它的父進(jìn)程那里繼承了打開的文件描述符。如不關(guān)閉,將會(huì)浪費(fèi)系統(tǒng)資源,造成進(jìn)程所在的文件系統(tǒng)無法卸下以及引起無法預(yù)料的錯(cuò)誤。按如下方法關(guān)閉它們:
for(i=0;i 關(guān)閉打開的文件描述符close(i);>
(5) 改變當(dāng)前工作目錄
進(jìn)程活動(dòng)時(shí),其工作目錄所在的文件系統(tǒng)不能卸下。一般需要將工作目錄改變到根目錄。對(duì)于需要轉(zhuǎn)儲(chǔ)核心,寫運(yùn)行日志的進(jìn)程將工作目錄改變到特定目錄如/tmpchdir("/")
(6)重設(shè)文件創(chuàng)建掩模
進(jìn)程從創(chuàng)建它的父進(jìn)程那里繼承了文件創(chuàng)建掩模。它可能修改守護(hù)進(jìn)程所創(chuàng)建的文件的存取位。為防止這一點(diǎn),將文件創(chuàng)建掩模清除:umask(0);
(7)處理SIGCHLD信號(hào)
處理SIGCHLD信號(hào)并不是必須的。但對(duì)于某些進(jìn)程,特別是服務(wù)器進(jìn)程往往在請(qǐng)求到來時(shí)生成子進(jìn)程處理請(qǐng)求。如果父進(jìn)程不等待子進(jìn)程結(jié)束,子進(jìn)程將成為僵尸進(jìn)程(zombie)從而占用系統(tǒng)資源。如果父進(jìn)程等待子進(jìn)程結(jié)束,將增加父進(jìn)程的負(fù)擔(dān),影響服務(wù)器進(jìn)程的并發(fā)性能。在Linux下可以簡單地將SIGCHLD信號(hào)的操作設(shè)為SIG_IGN。
signal(SIGCHLD,SIG_IGN);
這樣,內(nèi)核在子進(jìn)程結(jié)束時(shí)不會(huì)產(chǎn)生僵尸進(jìn)程。這一點(diǎn)與BSD4不同,BSD4下必須顯式等待子進(jìn)程結(jié)束才能釋放僵尸進(jìn)程。
三、創(chuàng)建守護(hù)進(jìn)程
在創(chuàng)建之前我們先了解setsid()使用:
#include <unistd.h> pid_t setsid(void);DESCRIPTIONsetsid() creates a new session if the calling process is not a processgroup leader. The calling process is the leader of the new session,the process group leader of the new process group, and has no control-ling tty. The process group ID and session ID of the calling processare set to the PID of the calling process. The calling process will bethe only process in this new process group and in this new session.//調(diào)用進(jìn)程必須是非當(dāng)前進(jìn)程組組長,調(diào)用后,產(chǎn)生一個(gè)新的會(huì)話期,且該會(huì)話期中只有一個(gè)進(jìn)程組,且該進(jìn)程組組長為調(diào)用進(jìn)程,沒有控制終端,新產(chǎn)生的group ID 和 session ID 被設(shè)置成調(diào)用進(jìn)程的PID
RETURN VALUEOn success, the (new) session ID of the calling process is returned.On error, (pid_t) -1 is returned, and errno is set to indicate theerror.現(xiàn)在根據(jù)上述步驟創(chuàng)建一個(gè)守護(hù)進(jìn)程:
以下程序是創(chuàng)建一個(gè)守護(hù)進(jìn)程,然后利用這個(gè)守護(hù)進(jìn)程每個(gè)一分鐘向daemon.log文件中寫入當(dāng)前時(shí)間
01#include <stdio.h>02#include <unistd.h>03#include <stdlib.h>04#include <time.h>05#include <fcntl.h>06#include <string.h>07#include <sys/stat.h>08#define ERR_EXIT(m) 09do10{11perror(m);12exit(EXIT_FAILURE);13}14while (0);15void creat_daemon(void);16int main(void)17{18time_t t;19int fd;20creat_daemon();21while(1){22fd = open("daemon.log",O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_APPEND,0644);23if(fd == -1)24ERR_EXIT("open error");25t = time(0);26char *buf = asctime(localtime(&t));27write(fd,buf,strlen(buf));28close(fd);29sleep(60);30}31return 0;32}33void creat_daemon(void)34{35pid_t pid;36pid = fork();37if( pid == -1)38ERR_EXIT("fork error");39if(pid > 0 )40exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);41if(setsid() == -1)42ERR_EXIT("SETSID ERROR");43chdir("/");44int i;45for( i = 0; i < 3; ++i)46{47close(i);48open("/dev/null", O_RDWR);49dup(0);50dup(0);51}52umask(0);53return;54}復(fù)制代碼#include <stdio.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <time.h>#include <fcntl.h>#include <string.h>#include <sys/stat.h>#define ERR_EXIT(m) do{perror(m);exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}while (0);void creat_daemon(void);int main(void){time_t t;int fd;creat_daemon();while(1){fd = open("daemon.log",O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_APPEND,0644);if(fd == -1)ERR_EXIT("open error");t = time(0);char *buf = asctime(localtime(&t));write(fd,buf,strlen(buf));close(fd);sleep(60);}return 0;}void creat_daemon(void){pid_t pid;pid = fork();if( pid == -1)ERR_EXIT("fork error");if(pid > 0 )exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);if(setsid() == -1)ERR_EXIT("SETSID ERROR");chdir("/");int i;for( i = 0; i < 3; ++i){close(i);open("/dev/null", O_RDWR);dup(0);dup(0);}umask(0);return;}結(jié)果:
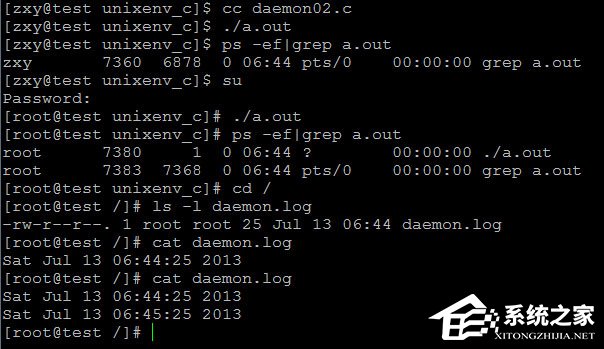
結(jié)果顯示:當(dāng)我一普通用戶執(zhí)行a.out時(shí),進(jìn)程表中并沒有出現(xiàn)新創(chuàng)建的守護(hù)進(jìn)程,但當(dāng)我以root用戶執(zhí)行時(shí),成功了,并在/目錄下創(chuàng)建了daemon.log文件,cat查看后確實(shí)每個(gè)一分鐘寫入一次。為什么只能root執(zhí)行,那是因?yàn)楫?dāng)我們創(chuàng)建守護(hù)進(jìn)程時(shí),已經(jīng)將當(dāng)前目錄切換我/目錄,所以當(dāng)我之后創(chuàng)建daemon.log文件是其實(shí)是在/目錄下,那肯定不行,因?yàn)槠胀ㄓ脩魶]有權(quán)限,或許你會(huì)問那為啥沒報(bào)錯(cuò)呢?其實(shí)是有出錯(cuò),只不過我們?cè)趧?chuàng)建守護(hù)進(jìn)程時(shí)已經(jīng)將標(biāo)準(zhǔn)輸入關(guān)閉并重定向到/dev/null,所以看不到錯(cuò)誤信息。
四、利用庫函數(shù)daemon()創(chuàng)建守護(hù)進(jìn)程
其實(shí)我們完全可以利用daemon()函數(shù)創(chuàng)建守護(hù)進(jìn)程,其函數(shù)原型:
#include <unistd.h>int daemon(int nochdir, int noclose);DESCRIPTIONThe daemon() function is for programs wishing to detach themselves fromthe controlling terminal and run in the background as system daemons. If nochdir is zero, daemon() changes the process’s current workingdirectory to the root directory ("/"); otherwise, If noclose is zero, daemon() redirects standard input, standard outputand standard error to /dev/null; otherwise, no changes are made tothese file descriptors.功能:創(chuàng)建一個(gè)守護(hù)進(jìn)程
參數(shù):
nochdir:=0將當(dāng)前目錄更改至“/”
noclose:=0將標(biāo)準(zhǔn)輸入、標(biāo)準(zhǔn)輸出、標(biāo)準(zhǔn)錯(cuò)誤重定向至“/dev/null”
返回值:
成功:0
失敗:-1
現(xiàn)在我們利用daemon()改寫剛才那個(gè)程序:
01#include <stdio.h>02#include <unistd.h>03#include <stdlib.h>04#include <time.h>05#include <fcntl.h>06#include <string.h>07#include <sys/stat.h>08#define ERR_EXIT(m) 09do10{11perror(m);12exit(EXIT_FAILURE);13}14while (0);15void creat_daemon(void);16int main(void)17{18time_t t;19int fd;20if(daemon(0,0) == -1)21ERR_EXIT("daemon error");22while(1){23fd = open("daemon.log",O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_APPEND,0644);24if(fd == -1)25ERR_EXIT("open error");26t = time(0);27char *buf = asctime(localtime(&t));28write(fd,buf,strlen(buf));29close(fd);30sleep(60);31}32return 0;33}復(fù)制代碼#include <stdio.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <time.h>#include <fcntl.h>#include <string.h>#include <sys/stat.h>#define ERR_EXIT(m) do{perror(m);exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}while (0);void creat_daemon(void);int main(void){time_t t;int fd;if(daemon(0,0) == -1)ERR_EXIT("daemon error");while(1){fd = open("daemon.log",O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_APPEND,0644);if(fd == -1)ERR_EXIT("open error");t = time(0);char *buf = asctime(localtime(&t));write(fd,buf,strlen(buf));close(fd);sleep(60);}return 0;}當(dāng)daemon(0,0)時(shí):
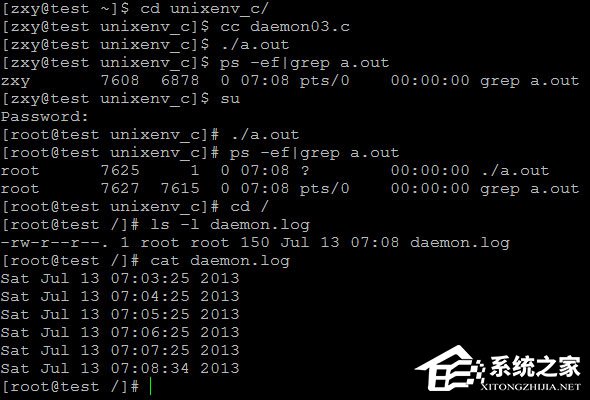
結(jié)果同剛才一樣,也是只有root才能成功,普通用戶執(zhí)行時(shí)看不到錯(cuò)誤信息
現(xiàn)在讓daemon(0,1),就是不關(guān)閉標(biāo)準(zhǔn)輸入輸出結(jié)果:
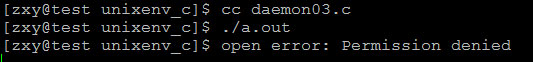
可以看到錯(cuò)誤信息
現(xiàn)在讓daemon(1,0),就是不重定向,結(jié)果如下:
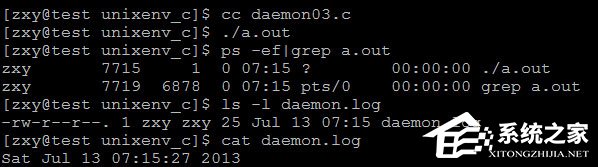
這次普通用戶執(zhí)行成功了,以為沒有切換到/目錄下,有權(quán)限
其實(shí)我們可以利用我們剛才寫的創(chuàng)建守護(hù)進(jìn)程程序默認(rèn)daemon()實(shí)現(xiàn):
代碼如下:
01#include <stdio.h>02#include <unistd.h>03#include <stdlib.h>04#include <time.h>05#include <fcntl.h>06#include <string.h>07#include <sys/stat.h>08#define ERR_EXIT(m) 09do10{11perror(m);12exit(EXIT_FAILURE);13}14while (0);15void creat_daemon(int nochdir, int noclose);16int main(void)17{18time_t t;19int fd;20creat_daemon(0,0);21while(1){22fd = open("daemon.log",O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_APPEND,0644);23if(fd == -1)24ERR_EXIT("open error");25t = time(0);26char *buf = asctime(localtime(&t));27write(fd,buf,strlen(buf));28close(fd);29sleep(60);30}31return 0;32}33void creat_daemon(int nochdir, int noclose)34{35pid_t pid;36pid = fork();37if( pid == -1)38ERR_EXIT("fork error");39if(pid > 0 )40exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);41if(setsid() == -1)42ERR_EXIT("SETSID ERROR");43if(nochdir == 0)44chdir("/");45if(noclose == 0){46int i;47for( i = 0; i < 3; ++i)48{49close(i);50open("/dev/null", O_RDWR);51dup(0);52dup(0);53}54umask(0);55return;56}復(fù)制代碼#include <stdio.h>#include <unistd.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <time.h>#include <fcntl.h>#include <string.h>#include <sys/stat.h>#define ERR_EXIT(m) do{perror(m);exit(EXIT_FAILURE);}while (0);void creat_daemon(int nochdir, int noclose);int main(void){time_t t;int fd;creat_daemon(0,0);while(1){fd = open("daemon.log",O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_APPEND,0644);if(fd == -1)ERR_EXIT("open error");t = time(0);char *buf = asctime(localtime(&t));write(fd,buf,strlen(buf));close(fd);sleep(60);}return 0;}void creat_daemon(int nochdir, int noclose){pid_t pid;pid = fork();if( pid == -1)ERR_EXIT("fork error");if(pid > 0 )exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);if(setsid() == -1)ERR_EXIT("SETSID ERROR");if(nochdir == 0)chdir("/");if(noclose == 0){int i;for( i = 0; i < 3; ++i){close(i);open("/dev/null", O_RDWR);dup(0);dup(0);}umask(0);return;}關(guān)于linux系統(tǒng)創(chuàng)建守護(hù)進(jìn)程的操作步驟就給大家講解到這里了,有此工作需求的伙伴,可以按照小編的步驟進(jìn)行創(chuàng)建。
相關(guān)文章:
1. fxksmdb.exe 是什么進(jìn)程 fxksmdb.exe可以關(guān)閉嗎2. 統(tǒng)信UOS個(gè)人版(V201030)正式發(fā)布 新增功能匯總3. 錄屏怎么保存gif動(dòng)圖? UOS錄屏生成Gif動(dòng)畫的技巧4. Win10專業(yè)版激活密鑰及激活教程5. Win10電腦制作定時(shí)關(guān)機(jī)代碼bat文件教程6. 華為筆記本如何重裝系統(tǒng)win10?華為筆記本重裝Win10系統(tǒng)步驟教程7. 如何修復(fù)Windows11/10上的Java虛擬機(jī)啟動(dòng)器錯(cuò)誤?8. Win10莫名其妙自動(dòng)安裝軟件怎么辦?Win10禁止電腦自動(dòng)安裝軟件教程9. 怎么刪除Win11中的臨時(shí)文件?Win11刪除臨時(shí)文件的兩種方法10. WmiPrvSE.exe是什么進(jìn)程?WMI Provider Host占用很高CPU的解決方法

 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備