關(guān)于python中readlines函數(shù)的參數(shù)hint的相關(guān)知識(shí)總結(jié)
>>> fr=open(’readme.txt’)>>> help(fr.readlines)Help on built-in function readlines: readlines(hint=-1, /) method of _io.TextIOWrapper instance Return a list of lines from the stream.hint can be specified to control the number of lines read: no more lines will be read if the total size (in bytes/characters) of all lines so far exceeds hint.Google翻譯
_io.TextIOWrapper 實(shí)例的 readlines(hint=-1, /) 方法 從流中返回行列表。 可以指定 hint 來(lái)控制讀取的行數(shù):如果到目前為止所有行的總大小(以字節(jié)/字符為單位)超過(guò)hint,則不會(huì)讀取更多行。
readme.txt中的內(nèi)容
>>> f=open(’readme.txt’)>>> f.readlines()[’1n’, ’22n’, ’n’, ’333’]
為了進(jìn)一步搞清楚hint,我寫(xiě)了一個(gè)函數(shù)來(lái)演示
readlines函數(shù)代碼def readlinesFile(filename,nbyte): ’’’ 探索f.readlines(i)中i的作用,典型的調(diào)用形式: readlinesFile(’readme.txt’,12) ’’’ for i in range(nbyte):f=open(filename)ss=f.readlines(i) if i==0:#如果hint=0,先把每一個(gè)元素輸出 textline=len(ss)#文件的總行數(shù) ntotalbyte=0#文件的總字?jǐn)?shù) nwritebyte=0#已經(jīng)寫(xiě)了的字節(jié)數(shù) for j in range(textline):#nwritebyte=ntotalbyte#已經(jīng)寫(xiě)了的字節(jié)數(shù)ntotalbyte=ntotalbyte+len(ss[j])rowbyte=0#已經(jīng)寫(xiě)了的新行的字節(jié)數(shù),用來(lái)記一行已經(jīng)輸出的字節(jié)個(gè)數(shù)while nwritebyte<ntotalbyte:#當(dāng)已寫(xiě)字節(jié)<總字節(jié)數(shù) print(f’{nwritebyte+1}:’,repr(ss[j][rowbyte])) #repr是為了輸出換行符 nwritebyte=nwritebyte+1 rowbyte=rowbyte+1 print(f’行數(shù)={textline},字?jǐn)?shù)={ntotalbyte}’)print(f’f.readlines{i}={ss}’) f.close()
輸出
>>> readlinesFile(’readme.txt’,12)1: ’1’2: ’n’3: ’2’4: ’2’5: ’n’6: ’n’7: ’3’8: ’3’9: ’3’行數(shù)=4,字?jǐn)?shù)=9f.readlines0=[’1n’, ’22n’, ’n’, ’333’]f.readlines1=[’1n’]f.readlines2=[’1n’, ’22n’]f.readlines3=[’1n’, ’22n’]f.readlines4=[’1n’, ’22n’]f.readlines5=[’1n’, ’22n’, ’n’]f.readlines6=[’1n’, ’22n’, ’n’, ’333’]f.readlines7=[’1n’, ’22n’, ’n’, ’333’]f.readlines8=[’1n’, ’22n’, ’n’, ’333’]f.readlines9=[’1n’, ’22n’, ’n’, ’333’]f.readlines10=[’1n’, ’22n’, ’n’, ’333’]f.readlines11=[’1n’, ’22n’, ’n’, ’333’]
總結(jié):1.hint 是要輸出顯示的字節(jié)數(shù)
2.hint 默認(rèn)等于-1,就是以列表的形式讀出所有內(nèi)容
3.hint = 0時(shí),效果等同于-1
4.hint 所指的字節(jié)數(shù)正好是換行符的話(huà),則實(shí)際輸出是 hint+1
更花哨的readlinesFile
def readlinesFile(filename,nbyte): ’’’ 探索f.readlines(i)中i是指什么,典型的調(diào)用形式: readlinesFile(’readme.txt’,12) ’’’ specialByte=[]#存儲(chǔ)特殊的字節(jié)數(shù)用 for i in range(nbyte):with open(filename) as f:#使用with語(yǔ)句就可以不使用f.close()了 ss=f.readlines(i) if(i==0):#如果hint=0,先把每一個(gè)元素輸出print(ss)textline=len(ss)#文件的總行數(shù)ntotalbyte=0#文件的總字?jǐn)?shù)nwritebyte=0#已經(jīng)寫(xiě)了的字節(jié)數(shù)for j in range(textline): #nwritebyte=ntotalbyte#已經(jīng)寫(xiě)了的字節(jié)數(shù) ntotalbyte=ntotalbyte+len(ss[j]) rowbyte=0#已經(jīng)寫(xiě)了的新行的字節(jié)數(shù),用來(lái)記一行已經(jīng)輸出的字節(jié)個(gè)數(shù) while nwritebyte<ntotalbyte:#當(dāng)已寫(xiě)字節(jié)<總字節(jié)數(shù)if(nwritebyte is ntotalbyte-1): specialByte.append(nwritebyte) print(f’033[0;31;47m{nwritebyte+1:2d}:’,repr(ss[j][rowbyte]),’033[0m’)#033[0m是字體和背景顏色設(shè)置,注意可能需要其他庫(kù)的支持else: print(f’{nwritebyte+1:2d}:’,repr(ss[j][rowbyte])) nwritebyte=nwritebyte+1 rowbyte=rowbyte+1print(f’033[0;31;40m行數(shù)={textline:2d},字?jǐn)?shù)={ntotalbyte:2d}033[0m’) if i in specialByte:print(f’033[0;31;47mf.readlines{i:<2d}={ss}033[0m’) #<是左對(duì)齊 else:print(f’f.readlines{i:<2d}={ss}’) #<是左對(duì)齊
效果
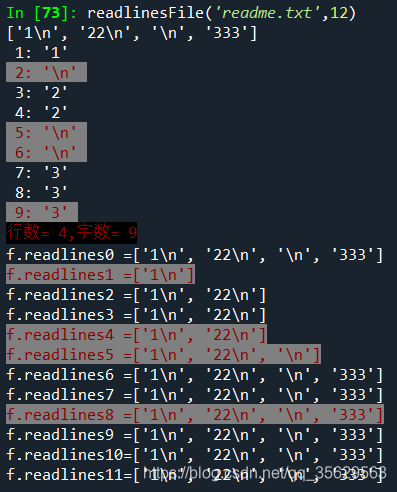
參考文章:https://www.jb51.net/article/206578.htm
到此這篇關(guān)于關(guān)于python中readlines函數(shù)的參數(shù)hint的相關(guān)知識(shí)總結(jié)的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關(guān)python readlines函數(shù)內(nèi)容請(qǐng)搜索好吧啦網(wǎng)以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關(guān)文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦網(wǎng)!
相關(guān)文章:
 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備