Python實(shí)現(xiàn)http接口自動(dòng)化測試的示例代碼
網(wǎng)上http接口自動(dòng)化測試Python實(shí)現(xiàn)有很多,我也是在慕課網(wǎng)上學(xué)習(xí)了相關(guān)課程,并實(shí)際操作了一遍,于是進(jìn)行一些總結(jié),便于以后回顧溫習(xí),有許多不完善的地方,希望大神們多多指教!
接口測試常用的工具有fiddler,postman,jmeter等,使用這些工具測試時(shí),需要了解常用的接口類型和區(qū)別,比如我用到的post和get請求,表面上看get用于獲取數(shù)據(jù)post用于修改數(shù)據(jù),兩者傳遞參數(shù)的方式也有不一樣,get是直接在url里通過?來連接參數(shù),而post則是把數(shù)據(jù)放在HTTP的包體內(nèi)(request body),兩者的本質(zhì)就是TCP鏈接,并無差別,但是由于HTTP的規(guī)定和瀏覽器/服務(wù)器的限制,導(dǎo)致他們在應(yīng)用過程中體現(xiàn)出一些不同。具體的可以參考此博文,講解的比較通俗易懂。這些在工具中可以直接選擇,python需要借助requests包。
確定好接口類型后,需要做的就是準(zhǔn)備測試數(shù)據(jù)和設(shè)計(jì)測試用例了,測試用例比如說可以判斷返回狀態(tài)響應(yīng)碼,或者對返回?cái)?shù)據(jù)進(jìn)行判別等,具體可以參考postman中的echo.collections,對于python可以用unittest來組織測試用例和添加斷言進(jìn)行判斷。而對于測試數(shù)據(jù)的準(zhǔn)備,需要做到數(shù)據(jù)和業(yè)務(wù)盡量分離,即將測試數(shù)據(jù)參數(shù)化,在工具中可以通過添加變量的形式實(shí)現(xiàn),對于python設(shè)計(jì)到的有關(guān)包有xlrd,json,如果需要連接數(shù)據(jù)庫還需要mysql。測試完成后生產(chǎn)報(bào)告或者發(fā)送郵件,也可以使用HTMLTestRunner和smtplib等。我也從這三大方面進(jìn)行總結(jié):
1. 接口方法實(shí)現(xiàn)和封裝
requests庫可以很好的幫助我們實(shí)現(xiàn)HTTP請求,API參考文檔,這里我創(chuàng)建了runmethod.py,里面包含RunMethod類:
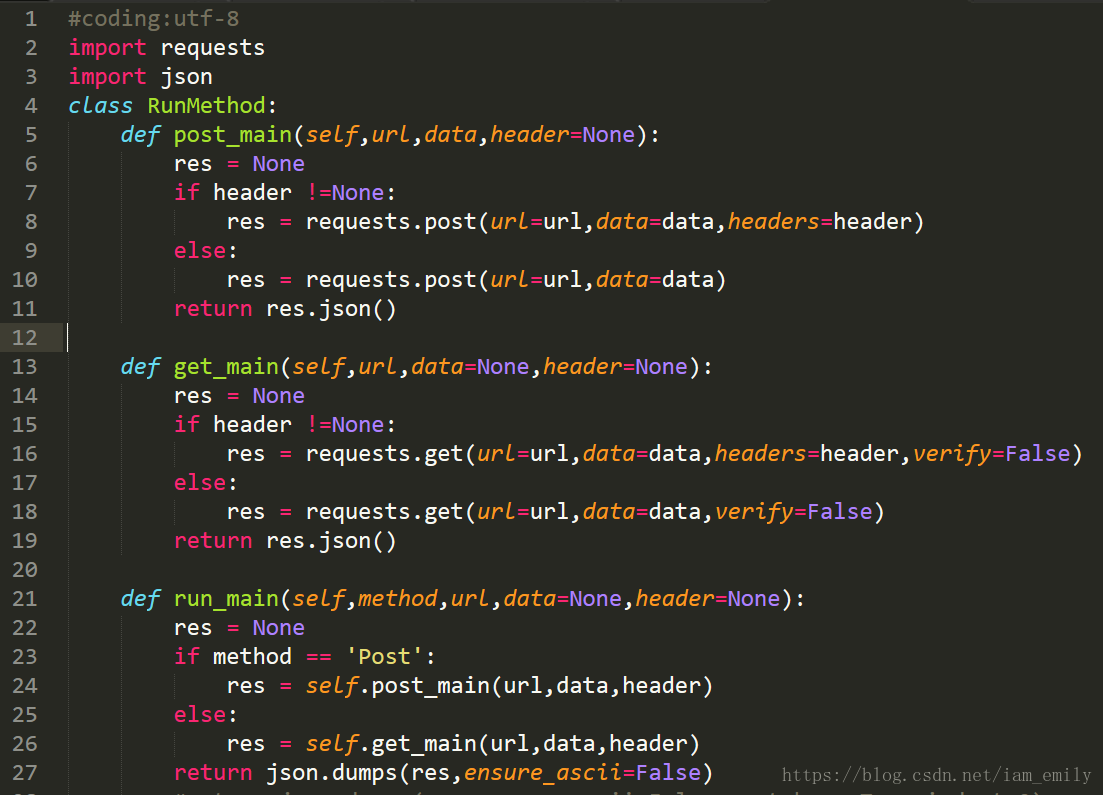
這里需要注意就是python默認(rèn)參數(shù)和可選參數(shù)要放在必選參數(shù)后面,對于相應(yīng)數(shù)據(jù)使用json格式進(jìn)行返回。參數(shù)verify=false表示忽略對 SSL 證書的驗(yàn)證。
2.組織測試和生成報(bào)告
使用unittest來組織測試、添加測試用例和斷言,測試報(bào)告可以下載HTMLTestRunner.py并放在python安裝路徑lib下即可,代碼如下:
#coding:utf-8import unittestimport jsonimport HTMLTestRunnerfrom mock import mock#from demo import RunMainfrom runmethod import RunMethodfrom mock_demo import mock_testimport osclass TestMethod(unittest.TestCase):def setUp(self):#self.run=RunMain()self.run = RunMethod()def test_01(self):url = ’http://coding.imooc.com/api/cate’data = {’timestamp’:’1507034803124’,’uid’:’5249191’,’uuid’:’5ae7d1a22c82fb89c78f603420870ad7’,’secrect’:’078474b41dd37ddd5efeb04aa591ec12’,’token’:’7d6f14f21ec96d755de41e6c076758dd’,’cid’:’0’,’errorCode’:1001}#self.run.run_main = mock.Mock(return_value=data)res = mock_test(self.run.run_main,data,url,'POST',data)#res = self.run.run_main(url,’POST’,data)print(res)self.assertEqual(res[’errorCode’],1001,'測試失敗')@unittest.skip(’test_02’)def test_02(self):url = ’http://coding.imooc.com/api/cate’data = {’timestamp’:’1507034803124’,’uid’:’5249191’,’uuid’:’5ae7d1a22c82fb89c78f603420870ad7’,’secrect’:’078474b41dd37ddd5efeb04aa591ec12’,’token’:’7d6f14f21ec96d755de41e6c076758dd’,’cid’:’0’}res = self.run.run_main(url,’GET’,data)self.assertEqual(res[’errorCode’],1006,'測試失敗')def test_03(self):url = ’http://coding.imooc.com/api/cate’data = {’timestamp’:’1507034803124’,’uid’:’5249191’,’uuid’:’5ae7d1a22c82fb89c78f603420870ad7’,’secrect’:’078474b41dd37ddd5efeb04aa591ec12’,’token’:’7d6f14f21ec96d755de41e6c076758dd’,’cid’:’0’,’status’:11}res = mock_test(self.run.run_main,data,url,’GET’,data)print(res)self.assertGreater(res[’status’],10,’測試通過’)if __name__ == ’__main__’:filepath = os.getcwd()+’report.html’fp = open(filepath,’wb+’)suite = unittest.TestSuite()suite.addTest(TestMethod(’test_01’))suite.addTest(TestMethod(’test_02’))suite.addTest(TestMethod(’test_03’))runner = HTMLTestRunner.HTMLTestRunner(stream=fp,title=’this is demo test’)runner.run(suite)#unittest.main()
這里setUp()方法用來在測試之前執(zhí)行,同樣的有tearDown()方法,測試case以test開頭進(jìn)行編寫,然后使用TestSuit類生成測試套件,將case添加進(jìn)去,運(yùn)行run suite即可。當(dāng)測試用例較多時(shí),可以生成多個(gè)測試類別,然后使用TestLoader().LoadTestsFromTestCase(測試類)生成測試用例,再加入testsuite執(zhí)行。在這里,我使用了學(xué)習(xí)到的mock方法,mock即模擬數(shù)據(jù),當(dāng)我們無法實(shí)際執(zhí)行獲得數(shù)據(jù)時(shí)可以使用mock方法,模擬生成我們需要判別的數(shù)據(jù),這里mock_test方法同樣進(jìn)行了封裝:
#coding:utf-8from mock import mockdef mock_test(mock_method,request_data,url,method,response_data):mock_method = mock.Mock(return_value=response_data)res = mock_method(url,method,request_data)return res
這里模擬的是self.run.run_main()方法,將這個(gè)方法的返回值設(shè)為response_data,而最終我們要判斷的是返回值res,可以結(jié)合test_02對比,
res = self.run.run_main(url,’GET’,data)
所以又需要傳入?yún)?shù)url,method,request_data,最后返回相應(yīng)數(shù)據(jù)即可,
res = mock_test(self.run.run_main,data,url,’GET’,data)
這里我假設(shè)返回的數(shù)據(jù)為data,隨意添加了幾個(gè)判斷條件errorCode==1001和status>10作為判斷依據(jù)。最后生成報(bào)告如下:

3 測試數(shù)據(jù)處理
這一部分主要包括設(shè)計(jì)測試數(shù)據(jù),數(shù)據(jù)提取和參數(shù)化,以及解決數(shù)據(jù)依賴。這里還是以慕課網(wǎng)上學(xué)習(xí)的例子為例,主要依據(jù)測試目的和使用流程來設(shè)計(jì),如下圖:
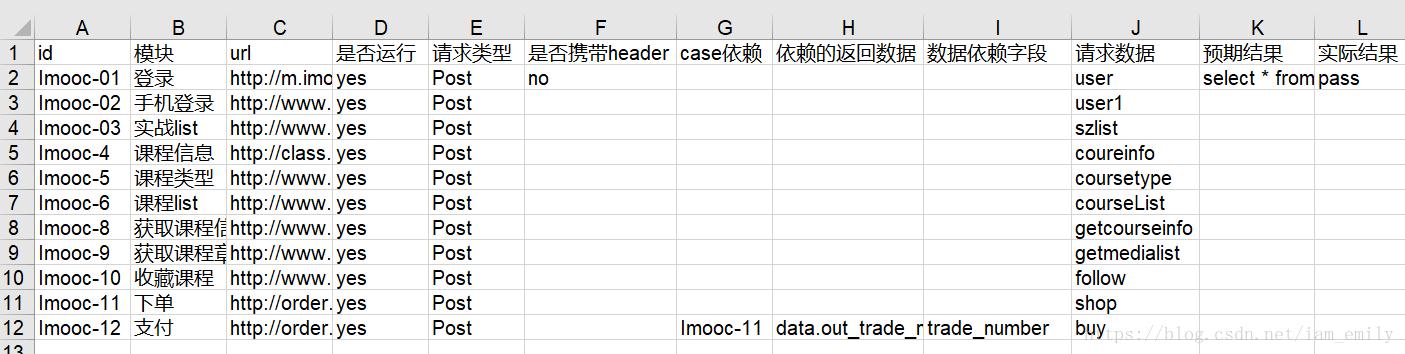
這里首先涉及到的就是對Excel表格的操作,導(dǎo)入相關(guān)庫import xlrd,先對如上表的測試用例進(jìn)行配置文件編寫:
class global_var:Id = ’0’request_name = ’1’url = ’2’run = ’3’request_way = ’4’header = ’5’case_depend = ’6’data_depend = ’7’field_depend = ’8’data = ’9’expect = ’10’result = ’11’
再定義返回該列的函數(shù),例如獲取caseId和URL:
def get_id():return global_var.Iddef get_url():return global_var.url
3.1操作Excel文件
然后我們再編寫操作Excel的模塊,主要包含了對Excel表格的操作,獲取表單、行、列、單元格內(nèi)容等。
import xlrdfrom xlutils.copy import copyclass OperationExcel:def __init__(self,file_name=None,sheet_id=None):if file_name:self.file_name = file_nameself.sheet_id = sheet_idelse:self.file_name = ’/dataconfig/case1.xls’self.sheet_id = 0self.data = self.get_data()#獲取sheets的內(nèi)容def get_data(self):data = xlrd.open_workbook(self.file_name)tables = data.sheets()[self.sheet_id]return tables#獲取單元格的行數(shù)def get_lines(self):tables = self.datareturn tables.nrows#獲取某一個(gè)單元格的內(nèi)容def get_cell_value(self,row,col):return self.data.cell_value(row,col)#寫入數(shù)據(jù)def write_value(self,row,col,value):’’’寫入excel數(shù)據(jù)row,col,value’’’read_data = xlrd.open_workbook(self.file_name)write_data = copy(read_data)sheet_data = write_data.get_sheet(0)sheet_data.write(row,col,value)write_data.save(self.file_name)
其中寫數(shù)據(jù)用于將運(yùn)行結(jié)果寫入Excel文件,先用copy復(fù)制整個(gè)文件,通過get_sheet()獲取的sheet有write()方法。
3.2操作json文件
對于請求數(shù)據(jù),我是根據(jù)關(guān)鍵字從json文件里取出字段,所以還需要json格式的數(shù)據(jù)文件,如下。對應(yīng)請求數(shù)據(jù)中的各個(gè)關(guān)鍵字:
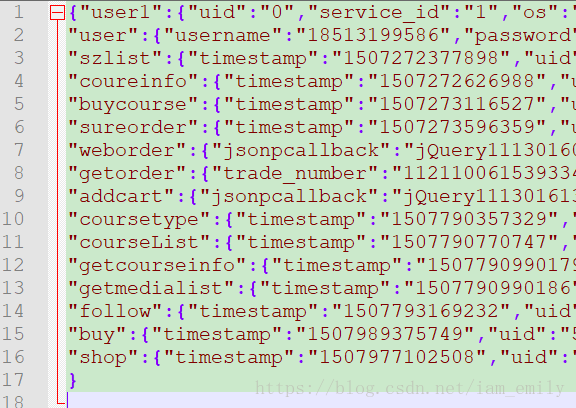
所以還需要編寫對應(yīng)操作json文件的模塊:
import jsonclass OperetionJson:def __init__(self,file_path=None):if file_path == None:self.file_path = ’/dataconfig/user.json’else:self.file_path = file_pathself.data = self.read_data()#讀取json文件def read_data(self):with open(self.file_path) as fp:data = json.load(fp)return data#根據(jù)關(guān)鍵字獲取數(shù)據(jù)def get_data(self,id):print(type(self.data))return self.data[id]
讀寫操作使用的是json.load(),json.dump() 傳入的是文件句柄。
3.3 獲得測試數(shù)據(jù)
在定義好Excel和json操作模塊后,我們將其應(yīng)用于我們的測試表單,定義一個(gè)獲取數(shù)據(jù)模塊:
from util.operation_excel import OperationExcelimport data.data_configfrom util.operation_json import OperetionJsonclass GetData:def __init__(self):self.opera_excel = OperationExcel()#去獲取excel行數(shù),就是我們的case個(gè)數(shù)def get_case_lines(self):return self.opera_excel.get_lines()#獲取是否執(zhí)行def get_is_run(self,row):flag = Nonecol = int(data_config.get_run())run_model = self.opera_excel.get_cell_value(row,col)if run_model == ’yes’:flag = Trueelse:flag = Falsereturn flag#是否攜帶headerdef is_header(self,row):col = int(data_config.get_header())header = self.opera_excel.get_cell_value(row,col)if header != ’’:return headerelse:return None#獲取請求方式def get_request_method(self,row):col = int(data_config.get_run_way())request_method = self.opera_excel.get_cell_value(row,col)return request_method#獲取urldef get_request_url(self,row):col = int(data_config.get_url())url = self.opera_excel.get_cell_value(row,col)return url#獲取請求數(shù)據(jù)def get_request_data(self,row):col = int(data_config.get_data())data = self.opera_excel.get_cell_value(row,col)if data == ’’:return Nonereturn data#通過獲取關(guān)鍵字拿到data數(shù)據(jù)def get_data_for_json(self,row):opera_json = OperetionJson()request_data = opera_json.get_data(self.get_request_data(row))return request_data#獲取預(yù)期結(jié)果def get_expcet_data(self,row):col = int(data_config.get_expect())expect = self.opera_excel.get_cell_value(row,col)if expect == ’’:return Nonereturn expectdef write_result(self,row,value):col = int(data_config.get_result())self.opera_excel.write_value(row,col,value)
該模塊將Excel操作類實(shí)例化后用于操作測試表單,分別獲得測試運(yùn)行所需的各種條件。
3.4 判斷條件
這里判斷一個(gè)case是否通過,是將實(shí)際結(jié)果和預(yù)期結(jié)果進(jìn)行對比,比如,狀態(tài)碼status是不是200,或者在返回?cái)?shù)據(jù)中查看是否含有某一字段:
import jsonimport operator as opclass CommonUtil:def is_contain(self, str_one,str_two):’’’判斷一個(gè)字符串是否再另外一個(gè)字符串中str_one:查找的字符串str_two:被查找的字符串’’’flag = None#先將返回的res進(jìn)行格式轉(zhuǎn)換,unicode轉(zhuǎn)成string類型if isinstance(str_one,unicode):str_one = str_one.encode(’unicode-escape’).decode(’string_escape’)return op.eq(str_one,str_two)if str_one in str_two:flag = Trueelse:flag = Falsereturn flagdef is_equal_dict(self,dict_one,dict_two):’’’判斷兩個(gè)字典是否相等’’’if isinstance(dict_one,str):dict_one = json.loads(dict_one)if isinstance(dict_two,str):dict_two = json.loads(dict_two)return op.eq(dict_one,dict_two)
所以我們獲得expec數(shù)據(jù)和相應(yīng)數(shù)據(jù),再調(diào)用這個(gè)類別的is_contain() 方法就能判斷。
3.5 數(shù)據(jù)依賴問題
當(dāng)我們要執(zhí)行的某個(gè)case的相應(yīng)數(shù)據(jù)依賴于前面某個(gè)case的返回?cái)?shù)據(jù)時(shí),我們需要對相應(yīng)數(shù)據(jù)進(jìn)行更新,比如case12的相應(yīng)數(shù)據(jù)request_data[數(shù)據(jù)依賴字段]的值應(yīng)該更新于case11的返回?cái)?shù)據(jù)response_data[依賴的返回字段] 。那么我們就需要先執(zhí)行case11拿到返回?cái)?shù)據(jù),再寫入case12的相應(yīng)數(shù)據(jù),首先對操作Excel的模塊進(jìn)行更新加入:
#獲取某一列的內(nèi)容def get_cols_data(self,col_id=None):if col_id != None:cols = self.data.col_values(col_id)else:cols = self.data.col_values(0)return cols#根據(jù)對應(yīng)的caseid找到對應(yīng)的行號(hào)def get_row_num(self,case_id):num = 0cols_data = self.get_cols_data()for col_data in cols_data:if case_id in col_data:return numnum = num+1#根據(jù)行號(hào),找到該行的內(nèi)容def get_row_values(self,row):tables = self.datarow_data = tables.row_values(row)return row_data#根據(jù)對應(yīng)的caseid 找到對應(yīng)行的內(nèi)容def get_rows_data(self,case_id):row_num = self.get_row_num(case_id)rows_data = self.get_row_values(row_num)return rows_data
即我們通過依賴的caseId找到對應(yīng)的行號(hào),拿到整行的內(nèi)容。我們默認(rèn)拿到列0的內(nèi)容(即caseId)循環(huán)整列找到依賴的caseId在第幾行,然后返回整行數(shù)據(jù),即實(shí)現(xiàn)方法get_rows_data(case_id) 。然后再去執(zhí)行和更新,我們編寫一個(gè)專門處理依賴數(shù)據(jù)的模塊,同時(shí),為了獲取依賴數(shù)據(jù),還需要對獲取數(shù)據(jù)模塊進(jìn)行更新如下:
#獲取依賴數(shù)據(jù)的keydef get_depend_key(self,row):col = int(data_config.get_data_depend())depent_key = self.opera_excel.get_cell_value(row,col)if depent_key == '':return Noneelse:return depent_key#判斷是否有case依賴def is_depend(self,row):col = int(data_config.get_case_depend())depend_case_id = self.opera_excel.get_cell_value(row,col)if depend_case_id == '':return Noneelse:return depend_case_id#獲取數(shù)據(jù)依賴字段def get_depend_field(self,row):col = int(data_config.get_field_depend())data = self.opera_excel.get_cell_value(row,col)if data == '':return Noneelse:return data
將方法應(yīng)用于專門處理依賴數(shù)據(jù)的模塊:
from util.operation_excel import OperationExcelfrom base.runmethod import RunMethodfrom data.get_data import GetDatafrom jsonpath_rw import jsonpath,parseclass DependdentData:def __init__(self,case_id):self.case_id = case_idself.opera_excel = OperationExcel()self.data = GetData()#通過case_id去獲取該case_id的整行數(shù)據(jù)def get_case_line_data(self):rows_data = self.opera_excel.get_rows_data(self.case_id)return rows_data#執(zhí)行依賴測試,獲取結(jié)果def run_dependent(self):run_method = RunMethod()row_num = self.opera_excel.get_row_num(self.case_id)request_data = self.data.get_data_for_json(row_num)#header = self.data.is_header(row_num)method = self.data.get_request_method(row_num)url = self.data.get_request_url(row_num)res = run_method.run_main(method,url,request_data)return json.loads(res)#返回?cái)?shù)據(jù)是字符串需要轉(zhuǎn)成json格式方便后續(xù)查詢#根據(jù)依賴的key去獲取執(zhí)行依賴測試case的響應(yīng),然后返回def get_data_for_key(self,row):depend_data = self.data.get_depend_key(row)response_data = self.run_dependent()json_exe = parse(depend_data)madle = json_exe.find(response_data)return [math.value for math in madle][0]
其中jsonpath用于找到多層級(jí)數(shù)據(jù),類似于xpath,即通過依賴字段表示的層級(jí)關(guān)系在返回?cái)?shù)據(jù)中找到對應(yīng)的值,最后再執(zhí)行該case時(shí)把數(shù)據(jù)更新。
3.6 主流程
把上述所有模塊導(dǎo)入,編寫主流程模塊:
from util.operation_excel import OperationExcelfrom base.runmethod import RunMethodfrom data.get_data import GetDatafrom jsonpath_rw import jsonpath,parseclass DependdentData:def __init__(self,case_id):self.case_id = case_idself.opera_excel = OperationExcel()self.data = GetData()#通過case_id去獲取該case_id的整行數(shù)據(jù)def get_case_line_data(self):rows_data = self.opera_excel.get_rows_data(self.case_id)return rows_data#執(zhí)行依賴測試,獲取結(jié)果def run_dependent(self):run_method = RunMethod()row_num = self.opera_excel.get_row_num(self.case_id)request_data = self.data.get_data_for_json(row_num)#header = self.data.is_header(row_num)method = self.data.get_request_method(row_num)url = self.data.get_request_url(row_num)res = run_method.run_main(method,url,request_data)return json.loads(res)#返回?cái)?shù)據(jù)是字符串需要轉(zhuǎn)成json格式方便后續(xù)查詢#根據(jù)依賴的key去獲取執(zhí)行依賴測試case的響應(yīng),然后返回def get_data_for_key(self,row):depend_data = self.data.get_depend_key(row)response_data = self.run_dependent()json_exe = parse(depend_data)madle = json_exe.find(response_data)return [math.value for math in madle][0]
這樣我們就完成了測試執(zhí)行,并對結(jié)果進(jìn)行了統(tǒng)計(jì),同時(shí)解決了數(shù)據(jù)依賴問題。
到此這篇關(guān)于Python實(shí)現(xiàn)http接口自動(dòng)化測試的示例代碼的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關(guān)Python http接口自動(dòng)化測試內(nèi)容請搜索好吧啦網(wǎng)以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關(guān)文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦網(wǎng)!
相關(guān)文章:
1. 用xslt+css讓RSS顯示的跟網(wǎng)頁一樣漂亮2. 利用CSS制作3D動(dòng)畫3. 使用Spry輕松將XML數(shù)據(jù)顯示到HTML頁的方法4. 存儲(chǔ)于xml中需要的HTML轉(zhuǎn)義代碼5. HTML5 Canvas繪制圖形從入門到精通6. 讓chatgpt將html中的圖片轉(zhuǎn)為base64方法示例7. CSS3實(shí)現(xiàn)動(dòng)態(tài)翻牌效果 仿百度貼吧3D翻牌一次動(dòng)畫特效8. 《CSS3實(shí)戰(zhàn)》筆記--漸變設(shè)計(jì)(一)9. html5手機(jī)觸屏touch事件介紹10. 讀大數(shù)據(jù)量的XML文件的讀取問題

 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備